How will 2022 be different from today when it comes to phishing attacks and other threats leveled against MSPs and their customers? During 2021, the scale of the phishing problem was huge. Credential phishing makes up 57% of malicious phishing campaigns, as reported by end users to the Cofense Phishing Defense Center.
Will 2022 be different? What other trends can MSPs expect? Let’s look at how the landscape of phishing threats is evolving, and how phishing will affect MSPs and their customers in 2022.
Phishing Affects MSPs in 2021
First, you must know your enemy: the threats that are reaching end users inboxes. Making the intelligence around phishing work for you is crucial. JetBlue CISO Tim Rohrbaugh says threat intelligence helps him get closer to real-time understanding of the threats that are coming, how they’re evolving, and how threat actors are re-using existing known tactics.
At Cofense we're looking at how phishing threats affect MSPs both tactically and strategically. Our network of almost 30 million human reporters helps reveal the known threats. We then analyze the phishing campaigns that are reaching MSP end users daily. And we are investigating the infrastructure and indicators of compromise (IOCs) that go into building those campaigns.
But we're also zooming the lens out and we're looking at overall trends in phishing threats. It’s important to identify the emerging tactics, techniques, and procedures (or TTPs) that threat actors use.
Since SEGs are bypassed so easily, we have found applying artificial intelligence, and particularly computer vision technology, to be highly effective to detect credential phishing and other complex phishing attacks. Computer Vision can spot fake graphics, fake brands and in turn analyze the final URL landing page to detect both known threats and unknown threats. AI doesn’t rely on deny lists. Instead, it can detect phishing attacks in real time. Multiple redirects and embedded URLs are detected. And the best AI systems continue to learn, increasing their effectiveness over time. Taken together, these technologies help MSPs focus their limited resources and defend against phishing.
2021 Top Threats
- Credential phishing, where today’s evolving attacks are sophisticated and difficult for humans to detect
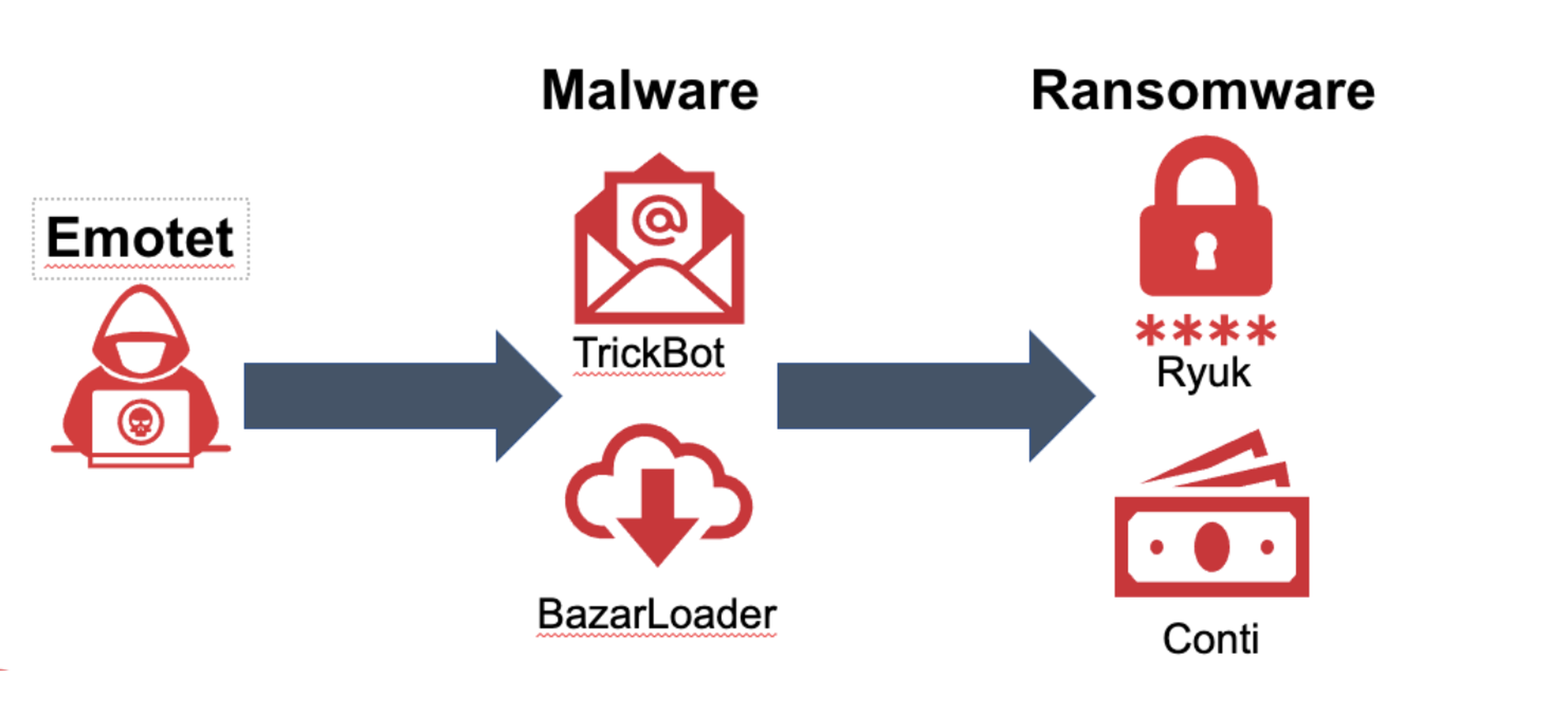
- Emotet, where Cofense Intelligence predicted the return of Emotet using new loaders
- Ransomware, where phishing is a precursor to ransomware attacks
We observe phishing attacks becoming more sophisticated year over year. And phishing attacks vary in volume during the year. However, the laws governing what we've traditionally seen in summer months and December into January did not occur in 2020 or thus far in 2021.
Previously we observed massive lulls at those times. While we saw a slight dip in 2021 during the summer months, with phishing volume dropping as travel ramped up, it was nothing compared to what we observed in past years. Likely this is due to the pandemic, forcing people away from taking their vacations. MSPs and their customers didn't step away from their business operations. Cyber criminals and threat actors, who in many areas of the world this is their full-time job, similarly didn't step away for their family vacations and time off.
Predictions for 2022
While text scams can be irritating, SMS phishing or “SMShing” continues not to be the big problem people were worried about. However, WhatsApp is being used for business email compromise or BEC scams, and other scams including gift cards. With WhatsApp, a threat actor can create a very convincing photo, and easily capture the names of CEOs and other people in authority, leading to credential and other types of attack.
MSPs should expect more O365 campaigns. This is truer every day as threat actors align campaigns with what Microsoft is doing, especially visually. Users are conditioned to approve apps, especially when presented with a Microsoft logo, which can look quite realistic. MSPs and their customers can be at risk if their users don’t know how they should be expecting legitimate alerts from their Microsoft configuration.
Further, a good percentage of initial phishing pages are being hosted in O365. If a threat actor compromises a small business, then the threat actor gets access to that account, including SharePoint and OneDrive, where they can create malware-infected documents and distribute them as attachments. These attacks are dangerous as they have a perfect email delivery scoring because they are coming from O365.
As MSPs and their customers adopt alternate messaging platforms such as Slack, or Teams, there is greater sharing across organizations. And these tools can connect to third parties, where phishing links can be sent across without using email. Because of the collaborative nature of document sharing on these team tools, there is a mix of external and internal document stores. This is a great setup for threat actors skilled at social engineering to obtain information.
We notice that threat actors will go where the users are, so if the other party does not have as robust anti-phishing discipline as yours, then the other party may be compromised. In 2022, this could affect MSPs and their customers when interacting with the joint teams they put together.
When it comes to BEC, we expect MSPs and their customers to see a rising volume of attacks. Signs are pointing to another round of high-profile arrests, and even extraditions, as government leaders become increasingly frustrated with the slow pace of justice.
While early BEC dollar amounts amounted to a nuisance, today they are becoming larger with extortion and Denial of Service implications (e.g., pipeline, food delivery chain).
Finally, the Emotet botnet just will not go away in 2022. Emotet is a precursor to ransomware, loading malware and waiting until the right time to detonate. An Emotet attack nearly always start with a phish. After its initial 2021 surge, Emotet went quiet, followed by a brief return, a government takedown with arrests, but now it has come back. Cofense Intelligence customers were warned Emotet would return with new malware delivery loaders, and that proved to be correct.
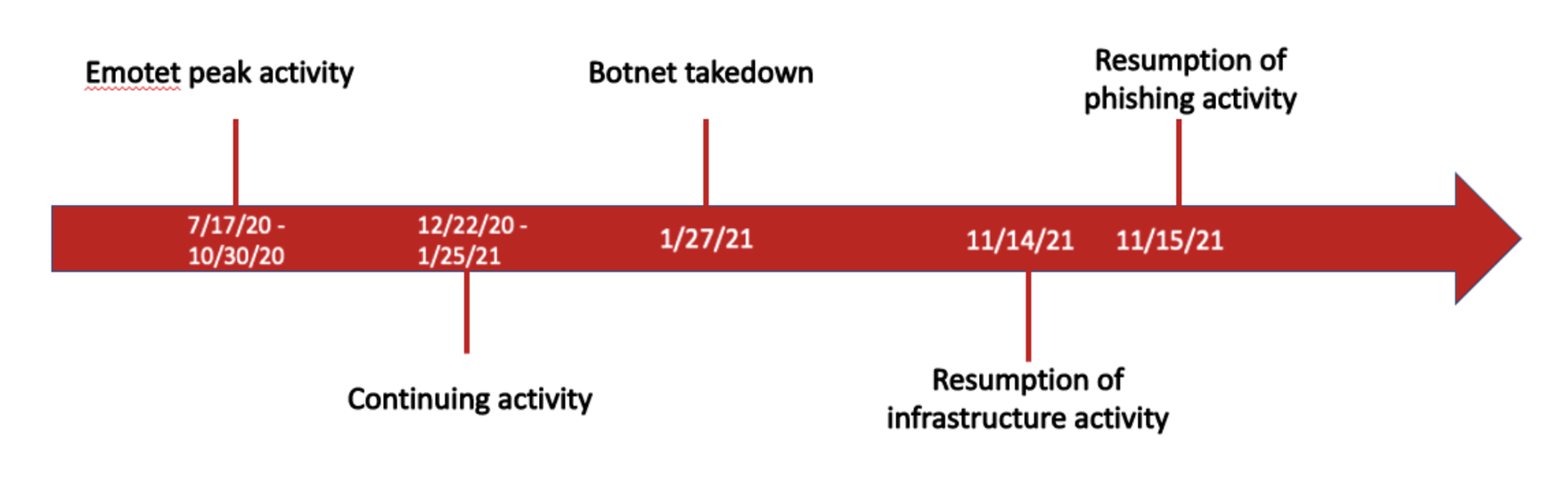
Most MSPs have rules in place to prevent Emotet. When Emotet got started it sent out password-protected ZIPs, but most MSPs block these attachments. The issue is not all suppliers in the chain also have robust attachment rules; this could be problematic for some MSPs and certain vertical industries. We predict Emotet will remain active and uninterrupted during 2022.
Summary
It is clear that MSPs and their customers will remain at risk during 2022 because phishing is a constantly evolving security problem. And the data shows that SEGs alone will not keep your customers safe from phishing attacks. Instead, an additional layer of security beyond the SEG is required.
Fortunately, MSPs now have access to modern phishing detection technologies. Using visual AI that detects and learns and is informed by threat intelligence of what real-world phishing looks like, it’s possible to stop what SEGs can’t. Contact our team to learn more about Cofense Protect MSP, designed specifically for MSPs. Book a demo to see how you can provide advanced phishing protection to keep your clients safe from today’s most sophisticated phishing attacks.
Rich Keith is senior product marketing manager at Cofense. Read more Cofense guest blogs here. Regularly contributed guest blogs are part of MSSP Alert’s sponsorship program.




